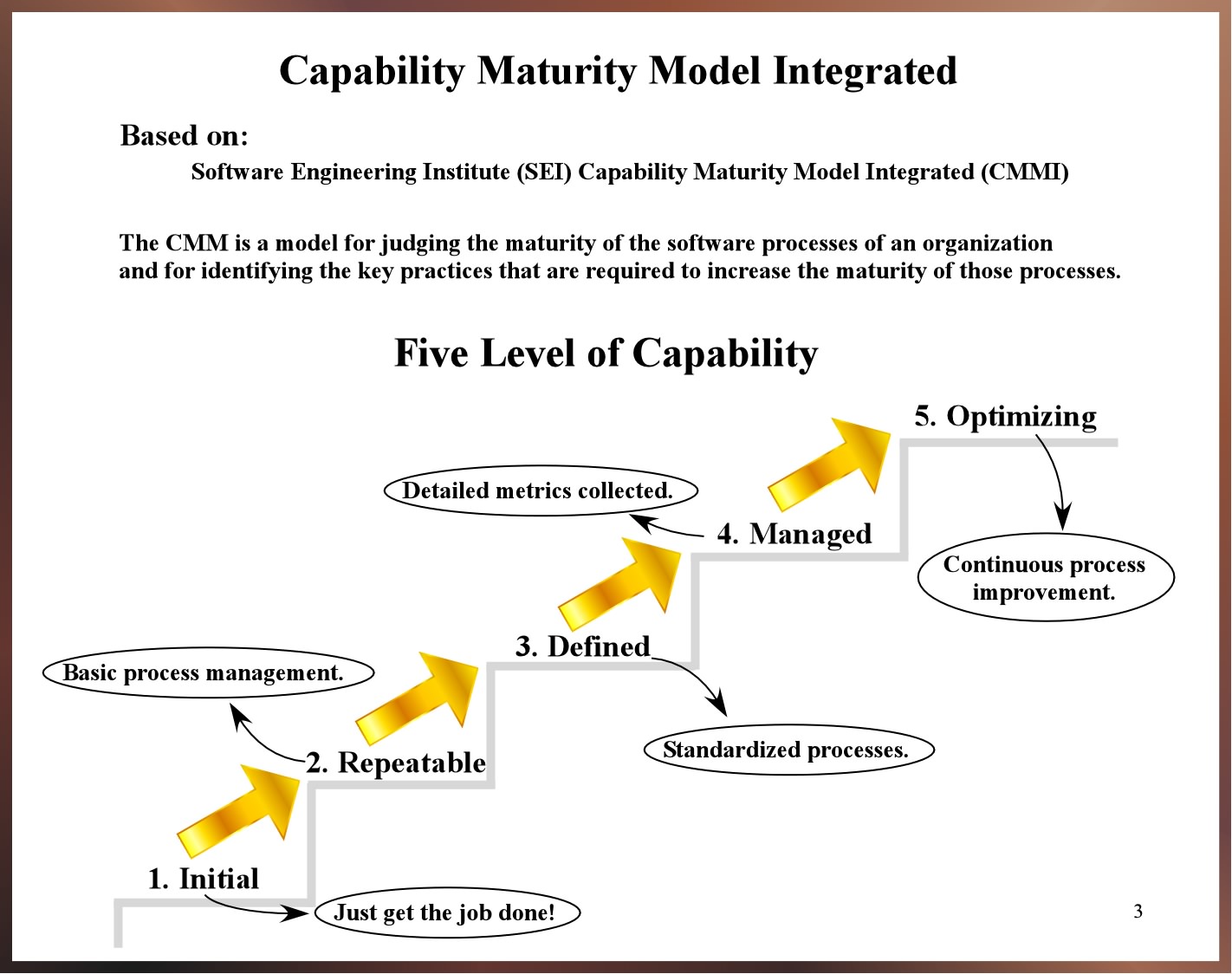
| 1. Initial | |
| At this state you just get the job done. There are few standards and the effort is frequently chaotic. Success depends on individual effort and heroics. There are no standards. Every company is considered to be working on this level if they have received no certification from SEI. | |
| 2. Repeatable | |
| Basic project management processes are established to track cost, schedule, and functionality. Standard process are used (stated steps in the SW development process, standard document templates, etc.) to insure the ability to repeat earlier successes. | |
| 3. Defined | |
| The company uses a standardized process for both management and SW engineering activities. There is a documented, standardized, published approach to be followed for each development activity. All projects must follow this approved process. | |
| 4. Managed | |
| Detailed measures of the SW development process and product quality are kept. The entire SW development process is very controlled. | |
| 5. Optimizing | |
| Continuous process improvement is conducted by using quantitative feedback from the SW development process. This feedback is used to lead to innovative ideas and technologies. | |