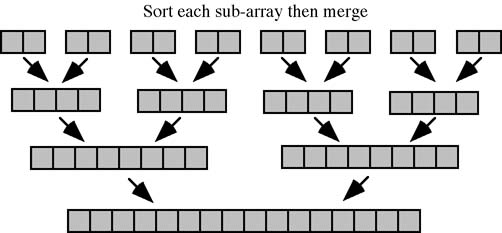
The basic idea behind Divide and Conquer Sorting is to divide the data into two smaller groups, sort these, then combine the two small sorted groups into one larger sorted group. Merge Sort is frequently used to sort very large collections of data stored on external devices. These techniques lend themselves to recursive calls and are frequently used in this way.
/***************************************/
/* MergeSort() */
/* */
/* Sort records on integer key using */
/* a merge sort. */
/***************************************/
void MergeSort(StructType DataArray[], int startIdx, int endIdx)
{
int start, end;
if(startIdx < endIdx) // If there is more than one item to sort
{
start = startIdx;
end = startIdx + ((endIdx - startIdx) / 2);
MergeSort(DataArray, start, end);
start = end + 1;
end = endIdx;
MergeSort(DataArray, start, end);
Merge(DataArray, startIdx, start - 1, start, end);
}
}
/***************************************/
/* Merge() */
/* Merge the two sections of the array */
/* using Insertion Sort treating one */
/* section as the sorted section and */
/* the other as the unsorted section. */
/***************************************/
void Merge(SortData Array1[], int start1, int end1,
int start2, int end2)
{
int i, j;
SortData temp;
int NotDone;
int Key;
for(i=start2; i<=end2; i++)
{
Key = Array1[i].key;
j = i;
NotDone = (Array1[j-1].key > Key);
temp = Array1[j];
while(NotDone)
{
// Slide all others to the right
Array1[j] = Array1[j-1];
j--;
if(j > start1)
NotDone = (Array1[j - 1].key > Key);
else
NotDone = FALSE;
}
// Put removed record into correct slot
Array1[j] = temp;
}
}